
Nozzles
Spray Nozzle Types and Features
Spray nozzles are classified based on the spray pattern they produce, their operating principles, and their areas of application. The most common types include:
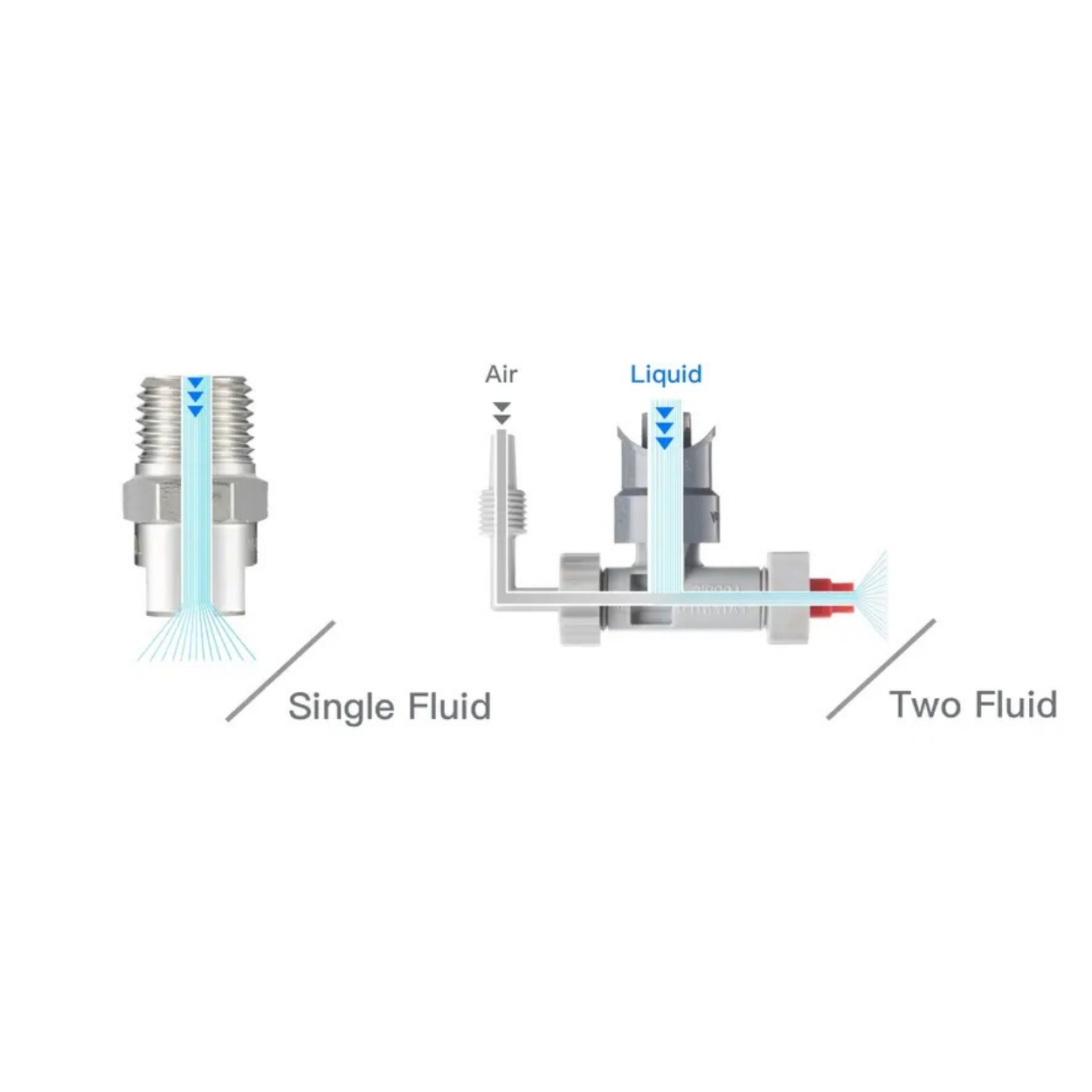
Solid Stream Nozzles: These nozzles discharge liquid in a narrow and powerful stream. They are typically used in high-impact cleaning, cutting, and applications requiring targeted fluid delivery. Spray angles typically range between 15° and 60°.
Flat Fan Nozzles: These nozzles produce a spray in the shape of a fan. They are ideal for applications where large surface areas need to be covered. Spray angles can vary from 0° to 110°, and flow rates range from 0.1 L/min to several hundred L/min.
Cone Nozzles: These nozzles produce a circular or conical spray pattern. Full cone nozzles ensure uniform coverage, while hollow cone nozzles produce finer droplets. Spray angles generally range between 30° and 180°.
Atomizing Nozzles (Fogging Nozzles): These nozzles generate very fine droplets (mist). They are used for humidification, cooling, and spraying chemicals. Average droplet sizes vary between 10 and 100 microns.
Pulsed Jet Nozzles: These nozzles deliver intermittent, high-velocity liquid pulses. They are effective in tough cleaning applications and surface treatments. Pulse frequencies are adjustable, and operating pressures can exceed 10 bar.

Applications and Numerical Data
Spray nozzles are used in a wide range of industrial and domestic settings:
Agriculture: Used for spraying pesticides, fertilizers, and irrigation. Agricultural spray nozzles typically feature spray angles between 80° and 110°, with droplet sizes ranging from 100 to 400 microns. Application rates vary from 50 to 500 liters per hectare.
Industrial Cleaning: Utilized in high-pressure washing systems. These nozzles can operate at pressures up to 100 bar and offer spray angles between 15° and 40°. Flow rates range from 5 L/min to 50 L/min.
Firefighting: Used to spray water or foam. Firefighting nozzles can deliver high flow rates (hundreds of liters per minute) and long ranges (over 30 meters).
Painting and Coating: Used to apply paint or coating materials evenly over surfaces. Air-assisted nozzles provide finer, smoother coatings, while airless nozzles are suitable for high-viscosity materials. Coating thickness can be controlled at the micron level.
Cooling and Humidification: Used in industrial processes, air conditioning systems, and greenhouses. Atomizing nozzles produce extremely fine droplets (10–50 microns) that remain suspended in the air, enhancing evaporation.
Conclusion
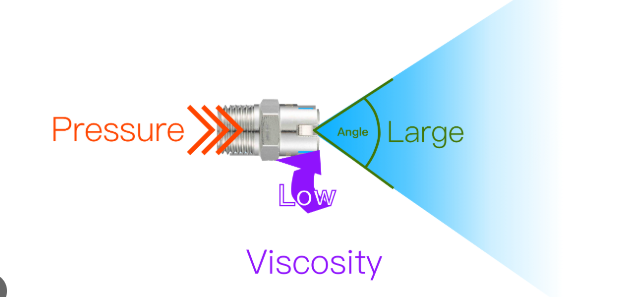
Spray nozzles are critical components that must be carefully selected according to performance requirements and application characteristics. Understanding key parameters such as flow rate, spray angle, droplet size, and pressure is essential for proper nozzle selection and optimizing system efficiency. With advances in technology, next-generation smart spray nozzles are being developed to offer more precise control, reduced liquid consumption, and greater efficiency.
| Nozul Tipi | Malzeme | Tipik Debi Aralığı (L/dk) | Tipik Püskürtme Açısı (°) |
| Düz Jet | Paslanmaz Çelik, Pirinç | 0.5 - 50 | 15 - 60 |
| Yelpaze Jet | Paslanmaz Çelik, Plastik | 0.1 - 100+ | 0 - 110 |
| Konik (Dolu) | Paslanmaz Çelik, Pirinç | 0.2 - 80 | 30 - 180 |
| Konik (Boş) | Paslanmaz Çelik, Plastik | 0.05 - 30 | 45 - 90 |
| Atomizer (Sisleme) | Paslanmaz Çelik, Plastik | 0.01 - 5 | 30 - 90 |










